spafe.frequencies.fundamental_frequencies#
Description : Implementation Fundamental Frequency Extraction Using the YIN-Algorithm.
Copyright (c) 2019-2024 Ayoub Malek. This source code is licensed under the terms of the BSD 3-Clause License. For a copy, see <https://github.com/SuperKogito/spafe/blob/master/LICENSE>.
- spafe.frequencies.fundamental_frequencies.compute_difference(x: ndarray, tau_max: int) ndarray[source]#
Compute difference function of data x according to [Guyot] [DeCheveigné] and [Box] . This essentially corresponds to equations (6) and (7) in [DeCheveigné]
- Parameters
x (numpy.ndarray) – audio array data.
tau_max (int) – integration window size.
- Returns
difference function resulting array.
- Return type
Note
\[ \begin{align}\begin{aligned}d_{t}(\tau) = \sum_{j=1}^{W}(x_{j} - x_{j+\tau})^{2}\\d_{t}(\tau) = r_{t}(0) + r_{t+\tau}(0) - 2 r_{t}(\tau)\end{aligned}\end{align} \]where \(d_{t}(\tau)\) is the difference function, \(r_{t}(\tau)\) is the autocorrelation.
This function use an accellerated convolution function fftconvolve from the Scipy package to compute the autocorrelation for faster processing.
While the brute force algorithm time complexity is O(n**2), the Wiener–Khinchin theorem allows computing the autocorrelation with two Fast Fourier transforms (FFT), with time complexity O(n log(n)).
- The steps for computing the autocorrelation according the Wiener–Khinchin theorem are as follows:
- \[ \begin{align}\begin{aligned}F_{R}(f) = FFT[X(t)]\\S(f) = F_{R}(f) + F^{*}_{R}(f)\\R(\tau) = IFFT[S(f)]\end{aligned}\end{align} \]
where IFFT is the inverse fast Fourier transform and the asterisk denotes complex conjugate.
References
- Box
: Box, G. E. P., Jenkins, G. M., Reinsel, G. C. (1994). Time Series Analysis: Forecasting and Control (3rd ed.). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice–Hall. ISBN 978-0130607744.
- spafe.frequencies.fundamental_frequencies.compute_cmnd(d_t: ndarray, tau: int) ndarray[source]#
Apply Cumulative Mean Normalized Difference Function (CMNDF) as in [Guyot] [DeCheveigné]. This corresponds to equation (8) in [DeCheveigné].
- Parameters
d_t (numpy.ndarray) – Difference function array.
tau (int) – length of data.
- Returns
cumulative mean normalized difference
- Return type
Note
\[\begin{split}d^{\prime}_{t}(\tau)=\left\{\begin{array}{l} 1, & \text{if } \tau = 0 \\ \frac{d_{t}(\tau)}{\frac{1}{\tau} \sum_{j=1}^{\tau} d_{t}(j)}, & \text{otherwise } \end{array}\right.\end{split}\]
- spafe.frequencies.fundamental_frequencies.get_pitch(cmdf: ndarray, tau_min: int, tau_max: int, harmonic_threshold: float = 0.1) float[source]#
Return fundamental period of a frame based on CMND function as implemented in [Guyot] [DeCheveigné].
- Parameters
cmdf (numpy.ndarray) – cumulative mean normalized difference
tau_min (int) – minimum period for speech.
tau_max (int) – maximum period for speech.
harmonic_threshold (float) – harmonicity threshold to determine if it is necessary to compute pitch frequency. (Default is 0.1).
- Returns
fundamental period if there is values under threshold, 0 otherwise
- Return type
(float)
- spafe.frequencies.fundamental_frequencies.compute_yin(sig: ndarray, fs: int, win_len: float = 0.03, win_hop: float = 0.015, low_freq: float = 50, high_freq: float = 3000, harmonic_threshold: float = 0.1) Tuple[ndarray, ndarray, ndarray, ndarray][source]#
Compute the fundamental frequency and harmonic rate according to the the Yin Algorithm [Guyot] [DeCheveigné].
- Parameters
sig (numpy.ndarray) – audio signal (list of float)
fs (int) – sampling rate (= average number of samples pro 1 second)
win_len (float) – size of the analysis window (in seconds) (Default is 0.03).
win_hop (float) – size of the lag between two consecutives windows (in seconds) (Default is 0.015).
low_freq (float) – Minimum fundamental frequency that can be detected (in Hertz) (Default is 50).
high_freq (float) – Maximum fundamental frequency that can be detected (in Hertz) (Default is 3000).
harmonic_threshold (float) – Threshold of detection. The yalgorithmù return the first minimum of the CMND fubction below this threshold. (Default is 0.1).
- Returns
- tuple include the following
pitches (numpy.array) : list of fundamental frequencies.
- harmonic_rates (numpy.array)list of harmonic rate values for each fundamental
frequency value (= confidence value).
argmins (numpy.array) : minimums of the Cumulative Mean Normalized DifferenceFunction.
times (numpy.array) : list of time of each estimation.
- Return type
(tuple)
References
- DeCheveigné(1,2,3,4,5,6)
: De Cheveigné, A., & Kawahara, H. (2002). YIN, a fundamental frequency estimator for speech and music. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 111(4), 1917-1930.
- Guyot(1,2,3,4)
: Guyot, P. (2018, April 19). Fast Python implementation of the Yin algorithm (Version v1.1.1). Zenodo. http://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.1220947
Examples
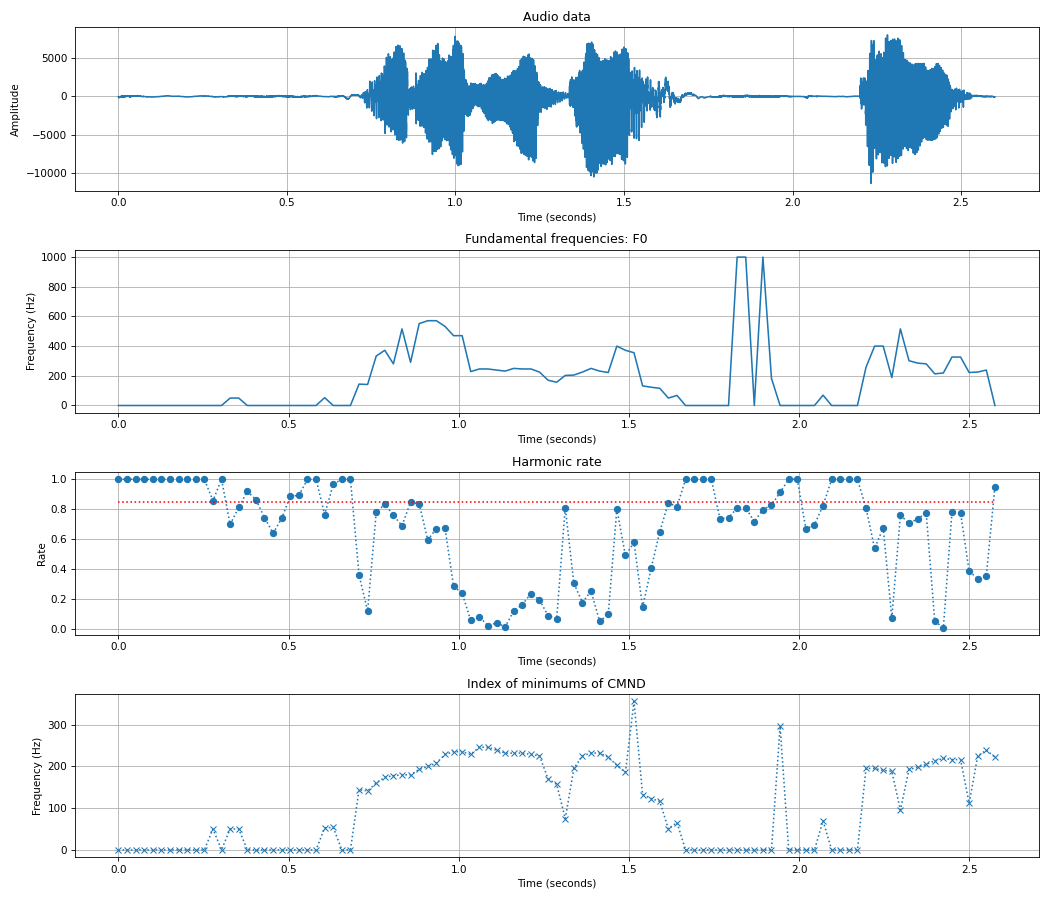
from scipy.io.wavfile import read from spafe.frequencies.fundamental_frequencies import compute_yin # read audio fpath = "../../../tests/data/test.wav" fs, sig = read(fpath) duration = len(sig) / fs harmonic_threshold = 0.85 pitches, harmonic_rates, argmins, times = compute_yin(sig, fs, win_len=0.050, win_hop=0.025, low_freq=50, high_freq=1000, harmonic_threshold=harmonic_threshold) # xaxis helper function gen_xaxis_times = lambda v, dt : [float(x) * dt / len(v) for x in range(0, len(v))] plt.figure(figsize=(14, 12)) plt.subplots_adjust(left=0.125, right=0.9, bottom=0.125, top=0.9, wspace=0.2, hspace=0.99) # plot audio data ax1 = plt.subplot(4, 1, 1) ax1.plot(gen_xaxis_times(sig, duration), sig) ax1.set_title("Audio data") ax1.set_ylabel("Amplitude") ax1.set_xlabel("Time (seconds)") plt.grid() # plot F0 ax2 = plt.subplot(4, 1, 2) ax2.plot(gen_xaxis_times(pitches, duration), pitches) ax2.set_title("Fundamental frequencies: F0") ax2.set_ylabel("Frequency (Hz)") ax2.set_xlabel("Time (seconds)") plt.grid() # plot Harmonic rate ax3 = plt.subplot(4, 1, 3, sharex=ax2) ax3.plot(gen_xaxis_times(harmonic_rates, duration), harmonic_rates, ":o") ax3.plot(gen_xaxis_times(harmonic_rates, duration), [harmonic_threshold] * len(harmonic_rates), "r:") ax3.set_title("Harmonic rate") ax3.set_ylabel("Rate") ax3.set_xlabel("Time (seconds)") plt.grid() # plot Index of minimums of CMND ax4 = plt.subplot(4, 1, 4, sharex=ax2) ax4.plot(gen_xaxis_times(argmins, duration), argmins, ":x") ax4.set_title("Index of minimums of CMND") ax4.set_ylabel("Frequency (Hz)") ax4.set_xlabel("Time (seconds)") plt.grid() plt.show()