spafe.features.mfcc#
Description : Mel and inverse Mel Features Cepstral Coefficients (MFCCs and IMFCCs) extraction algorithm implementation.
Copyright (c) 2019-2024 Ayoub Malek. This source code is licensed under the terms of the BSD 3-Clause License. For a copy, see <https://github.com/SuperKogito/spafe/blob/master/LICENSE>.
- spafe.features.mfcc.mel_spectrogram(sig, fs: int = 16000, pre_emph: bool = True, pre_emph_coeff: float = 0.97, window: Optional[SlidingWindow] = None, nfilts: int = 24, nfft: int = 512, low_freq: float = 0, high_freq: Optional[float] = None, scale: typing_extensions.Literal[ascendant, descendant, constant] = 'constant', fbanks: Optional[ndarray] = None, conversion_approach: typing_extensions.Literal[Oshaghnessy, Lindsay] = 'Oshaghnessy') ndarray[source]#
Compute the mel scale spectrogram.
- Parameters
sig (numpy.ndarray) – a mono audio signal (Nx1) from which to compute features.
fs (int) – the sampling frequency of the signal we are working with. (Default is 16000).
pre_emph (bool) – apply pre-emphasis if 1. (Default is True).
pre_emph_coeff (float) – pre-emphasis filter coefficient. (Default is 0.97).
window (SlidingWindow) – sliding window object. (Default is None).
nfilts (int) – the number of filters in the filter bank. (Default is 40).
nfft (int) – number of FFT points. (Default is 512).
low_freq (float) – lowest band edge of mel filters (Hz). (Default is 0).
high_freq (float) – highest band edge of mel filters (Hz). (Default is samplerate / 2).
scale (str) – monotonicity behavior of the filter banks. (Default is “constant”).
fbanks (numpy.ndarray) – filter bank matrix). (Default is None).
conversion_approach (str) – approach to use for conversion to the erb scale. (Default is “Oshaghnessy”).
- Returns
the mel spectrogram (num_frames x nfilts). (numpy.ndarray) : the mel center frequencies.
- Return type
Tip
scale: can take the following options [“constant”, “ascendant”, “descendant”].dct: can take the following options [1, 2, 3, 4].normalize: can take the following options [“mvn”, “ms”, “vn”, “mn”].conversion_approach: can take the following options [“Oshaghnessy”, “Beranek”, “Lindsay”]. Note that the use of different options than the default can lead to unexpected behavior/issues.
Note
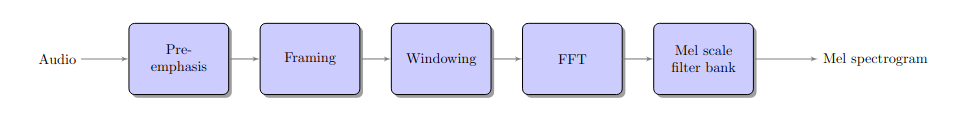
Architecture of Mel spectrogram extraction algorithm.#
Examples
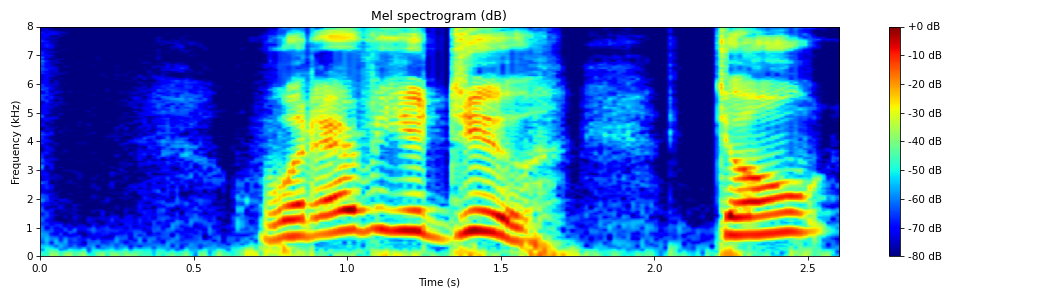
from spafe.features.mfcc import mel_spectrogram from spafe.utils.vis import show_spectrogram from spafe.utils.preprocessing import SlidingWindow from scipy.io.wavfile import read # read audio fpath = "../../../tests/data/test.wav" fs, sig = read(fpath) mSpec, _ = mel_spectrogram(sig, fs=fs, pre_emph=0, pre_emph_coeff=0.97, window=SlidingWindow(0.03, 0.015, "hamming"), nfilts=128, nfft=2048, low_freq=0, high_freq=fs/2) show_spectrogram(mSpec.T, fs, xmin=0, xmax=len(sig)/fs, ymin=0, ymax=(fs/2)/1000, dbf=80.0, xlabel="Time (s)", ylabel="Frequency (kHz)", title="Mel spectrogram (dB)", cmap="jet")
- spafe.features.mfcc.mfcc(sig: ndarray, fs: int = 16000, num_ceps: int = 13, pre_emph: bool = True, pre_emph_coeff: float = 0.97, window: Optional[SlidingWindow] = None, nfilts: int = 24, nfft: int = 512, low_freq: float = 0, high_freq: Optional[float] = None, scale: typing_extensions.Literal[ascendant, descendant, constant] = 'constant', dct_type: int = 2, use_energy=False, lifter: Optional[int] = None, normalize: Optional[typing_extensions.Literal[mvn, ms, vn, mn]] = None, fbanks: Optional[ndarray] = None, conversion_approach: typing_extensions.Literal[Oshaghnessy, Lindsay] = 'Oshaghnessy') ndarray[source]#
Compute MFCC features (Mel-frequency cepstral coefficients) from an audio signal. This function offers multiple approaches to features extraction depending on the input parameters. This MFCC implemenation is using FFT and can summarized in the following:
pre-empahsis
framing + Windowing
take the absolute value of the FFT
warp to a Mel frequency scale
take the DCT of the log-Mel-spectrum
return the first <num_ceps> components
- Parameters
sig (numpy.ndarray) – a mono audio signal (Nx1) from which to compute features.
fs (int) – the sampling frequency of the signal we are working with. (Default is 16000).
num_ceps (int) – number of cepstra to return. (Default is 13).
pre_emph (bool) – apply pre-emphasis if 1. (Default is True).
pre_emph_coeff (float) – pre-emphasis filter coefficient. (Default is 0.97).
window (SlidingWindow) – sliding window object. (Default is None).
nfilts (int) – the number of filters in the filter bank. (Default is 40).
nfft (int) – number of FFT points. (Default is 512).
low_freq (float) – lowest band edge of mel filters (Hz). (Default is 0).
high_freq (float) – highest band edge of mel filters (Hz). (Default is samplerate / 2).
scale (str) – monotonicity behavior of the filter banks. (Default is “constant”).
dct_type (int) – type of DCT used. (Default is 2).
use_energy (bool) – overwrite C0 with true log energy. (Default is False).
lifter (int) – apply liftering if not None. (Default is None).
normalize (str) – apply normalization if approach specified. (Default is None).
fbanks (numpy.ndarray) – filter bank matrix. (Default is None).
conversion_approach (str) – approach to use for conversion to the erb scale. (Default is “Oshaghnessy”).
- Returns
features - the MFFC features: num_frames x num_ceps
- Return type
Tip
scale: can take the following options [“constant”, “ascendant”, “descendant”].dct: can take the following options [1, 2, 3, 4].normalize: can take the following options [“mvn”, “ms”, “vn”, “mn”].conversion_approach: can take the following options [“Oshaghnessy”, “Lindsay”]. Note that the use of different options than the default can lead to unexpected behavior/issues.
Note
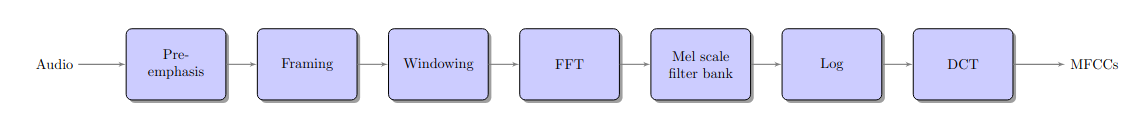
Architecture of Mel frequency cepstral coefficients extraction.#
- Examples
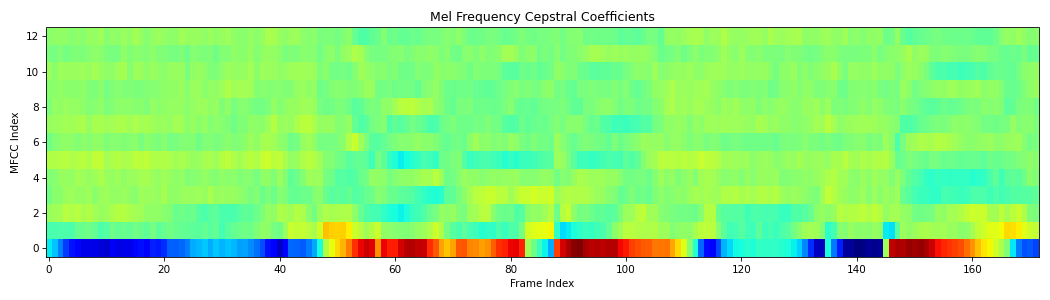
from scipy.io.wavfile import read from spafe.features.mfcc import mfcc from spafe.utils.preprocessing import SlidingWindow from spafe.utils.vis import show_features # read audio fpath = "../../../tests/data/test.wav" fs, sig = read(fpath) # compute mfccs and mfes mfccs = mfcc(sig, fs=fs, pre_emph=1, pre_emph_coeff=0.97, window=SlidingWindow(0.03, 0.015, "hamming"), nfilts=128, nfft=2048, low_freq=0, high_freq=8000, normalize="mvn") # visualize features show_features(mfccs, "Mel Frequency Cepstral Coefficients", "MFCC Index", "Frame Index")
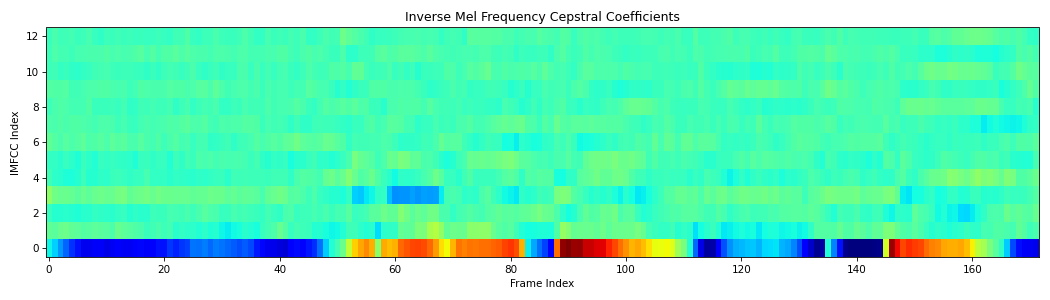
- spafe.features.mfcc.imfcc(sig: ndarray, fs: int = 16000, num_ceps=13, pre_emph: bool = True, pre_emph_coeff: float = 0.97, window: Optional[SlidingWindow] = None, nfilts: int = 24, nfft: int = 512, low_freq: float = 0, high_freq: Optional[float] = None, scale: typing_extensions.Literal[ascendant, descendant, constant] = 'constant', dct_type=2, use_energy=False, lifter=0, normalize=None, fbanks: Optional[ndarray] = None, conversion_approach: typing_extensions.Literal[Oshaghnessy, Lindsay] = 'Oshaghnessy') ndarray[source]#
Compute Inverse MFCC features from an audio signal.
- Parameters
sig (numpy.ndarray) – a mono audio signal (Nx1) from which to compute features.
fs (int) – the sampling frequency of the signal we are working with. (Default is 16000).
num_ceps (int) – number of cepstra to return. (Default is 13).
pre_emph (bool) – apply pre-emphasis if 1. (Default is True).
pre_emph_coeff (float) – pre-emphasis filter coefficient. (Default is 0.97).
window (SlidingWindow) – sliding window object. (Default is None).
nfilts (int) – the number of filters in the filter bank. (Default is 40).
nfft (int) – number of FFT points. (Default is 512).
low_freq (float) – lowest band edge of mel filters (Hz). (Default is 0).
high_freq (float) – highest band edge of mel filters (Hz). (Default is samplerate / 2).
scale (str) – monotonicity behavior of the filter banks. (Default is “constant”).
dct_type (int) – type of DCT used. (Default is 2).
use_energy (bool) – overwrite C0 with true log energy. (Default is False).
lifter (int) – apply liftering if not None. (Default is None).
normalize (str) – apply normalization approach specified. (Default is None).
fbanks (numpy.ndarray) – filter bank matrix. (Default is None).
conversion_approach (str) – approach to use for conversion to the erb scale. (Default is “Oshaghnessy”).
- Returns
features - the inverse MFFC features: num_frames x num_ceps
- Return type
Tip
scale: can take the following options [“constant”, “ascendant”, “descendant”].dct: can take the following options [1, 2, 3, 4].normalize: can take the following options [“mvn”, “ms”, “vn”, “mn”].conversion_approach: can take the following options [“Oshaghnessy”, “Lindsay”]. Note that the use of different options than the default can lead to unexpected behavior/issues.
Note

Architecture of inverse Mel frequency cepstral coefficients extraction algorithm.#
- Examples
from scipy.io.wavfile import read from spafe.features.mfcc import imfcc from spafe.utils.preprocessing import SlidingWindow from spafe.utils.vis import show_features # read audio fpath = "../../../tests/data/test.wav" fs, sig = read(fpath) # compute mfccs and mfes imfccs = imfcc(sig, fs=fs, pre_emph=1, pre_emph_coeff=0.97, window=SlidingWindow(0.03, 0.015, "hamming"), nfilts=128, nfft=2048, low_freq=0, high_freq=8000, normalize="mvn") # visualize features show_features(imfccs, "Inverse Mel Frequency Cepstral Coefficients", "IMFCC Index","Frame Index")