spafe.features.bfcc#
Description : Bark Frequency Cepstral Coefficients (BFCCs) extraction algorithm implementation.
Copyright (c) 2019-2024 Ayoub Malek. This source code is licensed under the terms of the BSD 3-Clause License. For a copy, see <https://github.com/SuperKogito/spafe/blob/master/LICENSE>.
- spafe.features.bfcc.intensity_power_law(w: ndarray) ndarray[source]#
Apply the intensity power law based on [Hermansky] .
- Parameters
w (numpy.ndarray) – signal information.
- Returns
array after intensity power law.
- Return type
Note
\[E(\omega) = \frac{(\omega^{2}+56.8 \times 10^{6}) \omega^{4}}{(\omega^{2}+6.3 \times 10^{6})^{2} \times (\omega^{2}+0.38 \times 10^{9})}\]
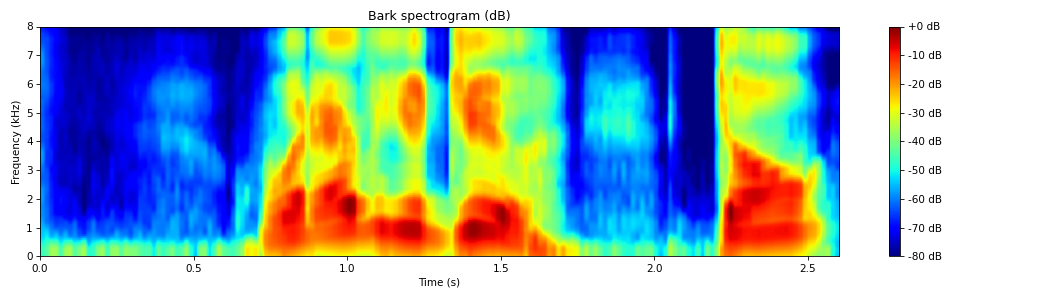
- spafe.features.bfcc.bark_spectrogram(sig: ndarray, fs: int = 16000, pre_emph: float = 0, pre_emph_coeff: float = 0.97, window: Optional[SlidingWindow] = None, nfilts: int = 24, nfft: int = 512, low_freq: float = 0, high_freq: Optional[float] = None, scale: typing_extensions.Literal[ascendant, descendant, constant] = 'constant', fbanks: Optional[ndarray] = None, conversion_approach: typing_extensions.Literal[Wang, Tjomov, Schroeder, Terhardt, Zwicker, Traunmueller] = 'Wang')[source]#
Compute the bark scale spectrogram.
- Parameters
sig (numpy.ndarray) – a mono audio signal (Nx1) from which to compute features.
fs (int) – the sampling frequency of the signal we are working with. (Default is 16000).
num_ceps (float) – number of cepstra to return. (Default is 13).
pre_emph (bool) – apply pre-emphasis if 1. (Default is True).
pre_emph_coeff (float) – pre-emphasis filter coefficient). (Default is 0.97).
window (SlidingWindow) – sliding window object. (Default is None).
nfilts (int) – the number of filters in the filter bank. (Default is 40).
nfft (int) – number of FFT points. (Default is 512).
low_freq (float) – lowest band edge of mel filters (Hz). (Default is 0).
high_freq (float) – highest band edge of mel filters (Hz). (Default is samplerate/2).
scale (str) – monotonicity behavior of the filter banks. (Default is “constant”).
fbanks (numpy.ndarray) – filter bank matrix. (Default is None).
conversion_approach (str) – bark scale conversion approach. (Default is “Wang”).
- Returns
(numpy.ndarray) : spectrogram matrix.
(numpy.ndarray) : fourrier transform.
- Return type
(tuple)
Tip
scale: can take the following options [“constant”, “ascendant”, “descendant”].conversion_approach: can take the following options [“Tjomov”,”Schroeder”, “Terhardt”, “Zwicker”, “Traunmueller”, “Wang”]. Note that the use of different options than the ddefault can lead to unexpected behavior/issues.
Note
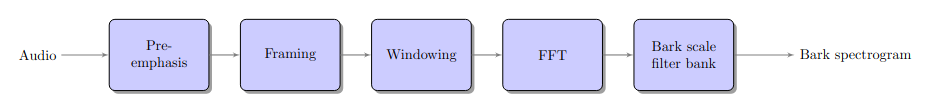
Architecture of Bark spectrogram computation algorithm.#
Examples
from spafe.features.bfcc import bark_spectrogram from spafe.utils.vis import show_spectrogram from spafe.utils.preprocessing import SlidingWindow from scipy.io.wavfile import read # read audio fpath = "../../../tests/data/test.wav" fs, sig = read(fpath) # compute bark spectrogram bSpec, bfreqs = bark_spectrogram(sig, fs=fs, pre_emph=0, pre_emph_coeff=0.97, window=SlidingWindow(0.03, 0.015, "hamming"), nfilts=128, nfft=2048, low_freq=0, high_freq=fs/2) # visualize spectrogram show_spectrogram(bSpec.T, fs=fs, xmin=0, xmax=len(sig)/fs, ymin=0, ymax=(fs/2)/1000, dbf=80.0, xlabel="Time (s)", ylabel="Frequency (kHz)", title="Bark spectrogram (dB)", cmap="jet")
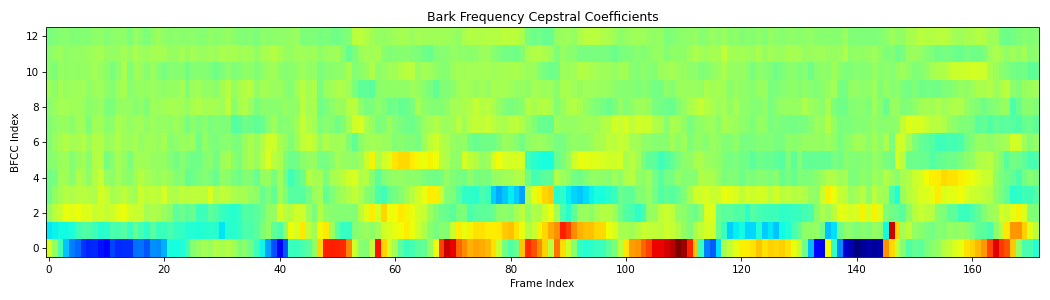
- spafe.features.bfcc.bfcc(sig: ndarray, fs: int = 16000, num_ceps: int = 13, pre_emph: bool = True, pre_emph_coeff: float = 0.97, window: Optional[SlidingWindow] = None, nfilts: int = 26, nfft: int = 512, low_freq: float = 0, high_freq: Optional[float] = None, scale: typing_extensions.Literal[ascendant, descendant, constant] = 'constant', dct_type: int = 2, use_energy: bool = False, lifter: Optional[int] = None, normalize: Optional[typing_extensions.Literal[mvn, ms, vn, mn]] = None, fbanks: Optional[ndarray] = None, conversion_approach: typing_extensions.Literal[Wang, Tjomov, Schroeder, Terhardt, Zwicker, Traunmueller] = 'Wang') ndarray[source]#
Compute the Bark Frequency Cepstral Coefficients (BFCCs) from an audio signal as described in [Kaminska].
- Parameters
sig (numpy.ndarray) – a mono audio signal (Nx1) from which to compute features.
fs (int) – the sampling frequency of the signal we are working with. (Default is 16000).
num_ceps (float) – number of cepstra to return. (Default is 13).
pre_emph (bool) – apply pre-emphasis if 1. (Default is True).
pre_emph_coeff (float) – pre-emphasis filter coefficient. (Default is 0.97).
window (SlidingWindow) – sliding window object. (Default is None).
nfilts (int) – the number of filters in the filter bank. (Default is 40).
nfft (int) – number of FFT points. (Default is 512).
low_freq (float) – lowest band edge of mel filters (Hz). (Default is 0).
high_freq (float) – highest band edge of mel filters (Hz). (Default is samplerate/2).
scale (str) – monotonicity behavior of the filter banks. (Default is “constant”).
dct_type (int) – type of DCT used. (Default is 2).
use_energy (int) – overwrite C0 with true log energy. (Default is 0).
lifter (int) – apply liftering if specified. (Default is None).
normalize (str) – apply normalization if approach specified. (Default is None).
fbanks (numpy.ndarray) – filter bank matrix. (Default is None).
conversion_approach (str) – bark scale conversion approach. (Default is “Wang”).
- Returns
2d array of BFCC features (num_frames x num_ceps).
- Return type
- Raises
ParameterError – if nfilts < num_ceps
Tip
dct: can take the following options [1, 2, 3, 4].normalize: can take the following options [“mvn”, “ms”, “vn”, “mn”].conversion_approach: can take the following options [“Tjomov”,”Schroeder”, “Terhardt”, “Zwicker”, “Traunmueller”, “Wang”]. Note that the use of different options than the ddefault can lead to unexpected behavior/issues.
Note

Architecture of Bark frequency cepstral coefficients extraction algorithm.#
References
- Kaminska
: Kamińska, D. & Sapiński, T. & Anbarjafari, G. (2017). Efficiency of chosen speech descriptors in relation to emotion recognition. EURASIP Journal on Audio Speech and Music Processing. 2017. 10.1186/s13636-017-0100-x.
- Examples
from scipy.io.wavfile import read from spafe.features.bfcc import bfcc from spafe.utils.preprocessing import SlidingWindow from spafe.utils.vis import show_features # read audio fpath = "../../../tests/data/test.wav" fs, sig = read(fpath) # compute bfccs bfccs = bfcc(sig, fs=fs, pre_emph=1, pre_emph_coeff=0.97, window=SlidingWindow(0.03, 0.015, "hamming"), nfilts=128, nfft=2048, low_freq=0, high_freq=8000, normalize="mvn") # visualize features show_features(bfccs, "Bark Frequency Cepstral Coefficients", "BFCC Index", "Frame Index")