spafe.features.lfcc#
Description : Linear Frequency Cepstral Coefficients (LFCCs) extraction algorithm implementation.
Copyright (c) 2019-2024 Ayoub Malek. This source code is licensed under the terms of the BSD 3-Clause License. For a copy, see <https://github.com/SuperKogito/spafe/blob/master/LICENSE>.
- spafe.features.lfcc.linear_spectrogram(sig: ndarray, fs: int = 16000, pre_emph: bool = True, pre_emph_coeff: float = 0.97, window: Optional[SlidingWindow] = None, nfilts: int = 24, nfft: int = 512, low_freq: float = 0, high_freq: Optional[float] = None, scale: typing_extensions.Literal[ascendant, descendant, constant] = 'constant', fbanks: Optional[ndarray] = None) ndarray[source]#
Compute the mel scale spectrogram.
- Parameters
sig (numpy.ndarray) – a mono audio signal (Nx1) from which to compute features.
fs (int) – the sampling frequency of the signal we are working with. (Default is 16000).
pre_emph (bool) – apply pre-emphasis if 1. (Default is 1).
pre_emph_coeff (float) – pre-emphasis filter coefficient. (Default is 0.97).
window (SlidingWindow) – sliding window object. (Default is None).
nfilts (int) – the number of filters in the filter bank. (Default is 40).
nfft (int) – number of FFT points. (Default is 512).
low_freq (float) – lowest band edge of mel filters (Hz). (Default is 0).
high_freq (float) – highest band edge of mel filters (Hz). (Default is samplerate / 2).
scale (str) – monotonicity behavior of the filter banks. (Default is “constant”).
fbanks (numpy.ndarray) – filter bank matrix. (Default is None).
- Returns
features - the LFFC features: num_frames x num_ceps
- Return type
Tip
scale: can take the following options [“constant”, “ascendant”, “descendant”].
Note
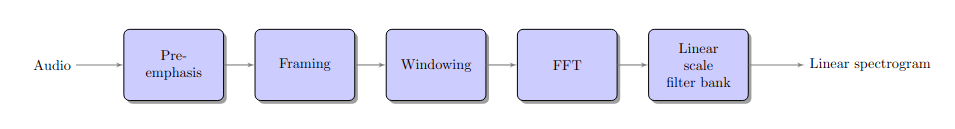
Architecture of linear scale spectrogram extraction algorithm.#
Examples
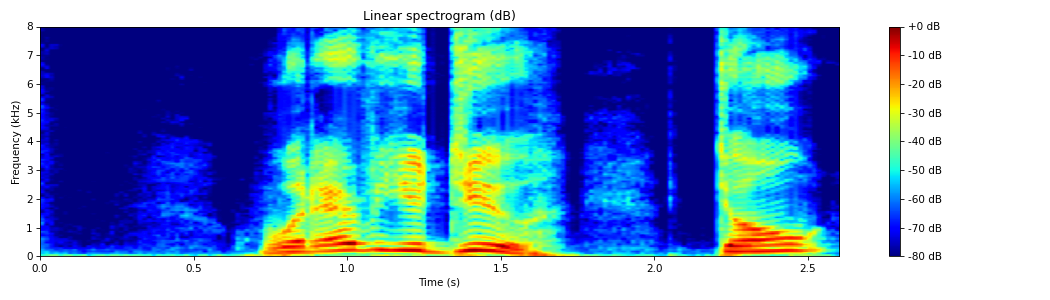
from spafe.features.lfcc import linear_spectrogram from spafe.utils.vis import show_spectrogram from spafe.utils.preprocessing import SlidingWindow from scipy.io.wavfile import read # read audio fpath = "../../../tests/data/test.wav" fs, sig = read(fpath) # compute spectrogram lSpec, lfreqs = linear_spectrogram(sig, fs=fs, pre_emph=0, pre_emph_coeff=0.97, window=SlidingWindow(0.03, 0.015, "hamming"), nfilts=128, nfft=2048, low_freq=0, high_freq=fs/2) # visualize spectrogram show_spectrogram(lSpec.T, fs, xmin=0, xmax=len(sig)/fs, ymin=0, ymax=(fs/2)/1000, dbf=80.0, xlabel="Time (s)", ylabel="Frequency (kHz)", title="Linear spectrogram (dB)", cmap="jet")
- spafe.features.lfcc.lfcc(sig, fs: int = 16000, num_ceps=13, pre_emph: bool = True, pre_emph_coeff: float = 0.97, window: Optional[SlidingWindow] = None, nfilts: int = 24, nfft: int = 512, low_freq: float = 0, high_freq: Optional[float] = None, scale: typing_extensions.Literal[ascendant, descendant, constant] = 'constant', dct_type=2, use_energy=False, lifter: Optional[int] = None, normalize: Optional[typing_extensions.Literal[mvn, ms, vn, mn]] = None, fbanks: Optional[ndarray] = None)[source]#
Compute the linear-frequency cepstral coefficients (GFCC features) from an audio signal as described in [Sehili].
- Parameters
sig (numpy.ndarray) – a mono audio signal (Nx1) from which to compute features.
fs (int) – the sampling frequency of the signal we are working with. (Default is 16000).
num_ceps (int) – number of cepstra to return. (Default is 13).
pre_emph (bool) – apply pre-emphasis if 1. (Default is 1).
pre_emph_coeff (float) – pre-emphasis filter coefficient. (Default is 0.97).
window (SlidingWindow) – sliding window object. (Default is None).
nfilts (int) – the number of filters in the filter bank. (Default is 40).
nfft (int) – number of FFT points. (Default is 512).
low_freq (float) – lowest band edge of mel filters (Hz). (Default is 0).
high_freq (float) – highest band edge of mel filters (Hz). (Default is samplerate / 2).
scale (str) – monotonicity behavior of the filter banks. (Default is “constant”).
dct_type (int) – type of DCT used. (Default is 2).
use_energy (bool) – overwrite C0 with true log energy. (Default is 0).
lifter (int) – apply liftering if specified. (Default is None).
normalize (str) – apply normalization if approach provided. (Default is None).
fbanks (numpy.ndarray) – filter bank matrix. (Default is None).
- Returns
2d array of LFCC features (num_frames x num_ceps).
- Return type
Tip
scale: can take the following options [“constant”, “ascendant”, “descendant”].dct: can take the following options [1, 2, 3, 4].normalize: can take the following options [“mvn”, “ms”, “vn”, “mn”].
Note
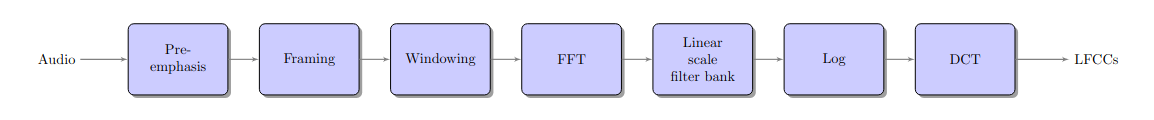
Architecture of linear frequency cepstral coefficients extraction algorithm.#
Examples
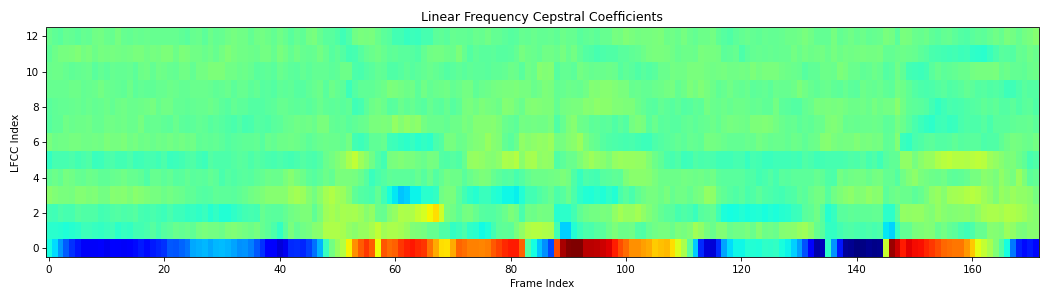
from scipy.io.wavfile import read from spafe.features.lfcc import lfcc from spafe.utils.preprocessing import SlidingWindow from spafe.utils.vis import show_features # read audio fpath = "../../../tests/data/test.wav" fs, sig = read(fpath) # compute lfccs lfccs = lfcc(sig, fs=fs, pre_emph=1, pre_emph_coeff=0.97, window=SlidingWindow(0.03, 0.015, "hamming"), nfilts=128, nfft=2048, low_freq=0, high_freq=8000, normalize="mvn") # visualize features show_features(lfccs, "Linear Frequency Cepstral Coefficients", "LFCC Index", "Frame Index")
References
- Sehili
: Sehili, A. & Istrate, B. & Boudy, J. (2022). Primary Investigation of Sound Recognition for a domotic application using Support Vector.
