spafe.features.pncc#
Description : Power-Normalized Cepstral Coefficients (PNCCs) extraction algorithm implementation.
Copyright (c) 2019-2024 Ayoub Malek. This source code is licensed under the terms of the BSD 3-Clause License. For a copy, see <https://github.com/SuperKogito/spafe/blob/master/LICENSE>.
- spafe.features.pncc.medium_time_power_calculation(P: ndarray, M: int = 2) ndarray[source]#
Compute the medium time power calulations according to [Kim] .
- Parameters
P (numpy.ndarray) – signal stft power.
M (int) – the temporal integration factor.
- Returns
medium time power values.
- Return type
Note
\[\tilde{Q}[m, l]=\frac{1}{2 M+1} \sum_{m^{\prime}=m-M}^{m+M} P[m^{\prime}]\]where \(\tilde{Q}\) is the medium time power, \(P\) is the power, \(m\) is the frame index, \(l\) is te channel index and \(M\) is the temporal integration factor.
- spafe.features.pncc.asymmetric_lowpass_filtering(Q_tilde_in: ndarray, lm_a: float = 0.999, lm_b: float = 0.5) ndarray[source]#
Apply asymmetric lowpass filter according to [Kim] .
- Parameters
Q_tilde_in (numpy.ndarray) – rectified signal.
lm_a (float) – filter parameter; lambda a.
lm_b (float) – filter parameter; lambda b.
- Returns
filtered signal.
- Return type
Note
\[\begin{split}\tilde{Q}_{out}[m, l]=\left\{\begin{array}{l} \lambda_{a}\tilde{Q}_{out}[m-1, l]+(1-\lambda_{a})\tilde{Q}_{in}[m, l], & \text{if } \tilde{Q}_{in}[m, l]\geq \tilde{Q}_{out}[m-1, l] \\ \lambda_{b}\tilde{Q}_{out}[m-1, l]+(1-\lambda_{b})\tilde{Q}_{in}[m, l], & \text{if } \tilde{Q}_{in}[m, l]<\tilde{Q}_{out}[m-1, l] \end{array}\right.\end{split}\]where \(\tilde{Q}_{in}\) and \(\tilde{Q}_{out}\) are arbitrary input and output, \(\lambda_{a}\) and \(\lambda_{b}\) are filter related parameters, \(m\) is the frame index, \(l\) is the channel index.
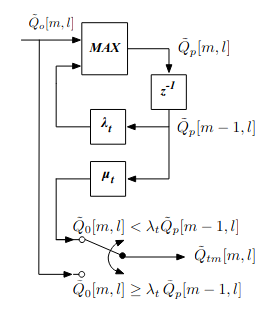
- spafe.features.pncc.temporal_masking(Q_tilde_0: ndarray, lam_t: float = 0.85, myu_t: float = 0.2) ndarray[source]#
- Parameters
Q_tilde_0 (numpy.ndarray) – rectified signal.
lam_t (float) – the forgetting factor-
myu_t (float) – the recognition accuracy.
- Returns
Q_tilde_tm = temporal_masking(Q_tilde_0)
- Return type
- spafe.features.pncc.weight_smoothing(R_tilde: ndarray, Q_tilde: ndarray, nfilts: int = 128, N: int = 4) ndarray[source]#
Apply spectral weight smoothing according to [Kim].
- Parameters
R_tilde (numpy.ndarray) –
Q_tilde (numpy.ndarray) – medium time power
nfilts (int) – total number of channels / filters
N (int) –
- Returns
time-averaged frequency-averaged transfer function.
- Return type
Note
\[\tilde{S}[m, l]=(\frac{1}{l_{2}-l_{1}+1} \sum_{l^{\prime}=l_{1}}^{l_{2}} \frac{\tilde{R}[m, l^{\prime}]}{\tilde{Q}[m, l^{\prime}]})\]where \(l_{2}=\min (l+N, L)\) and \(l_{1}=\max (l-N, 1)\), and \(L\) is the total number of channels, and \(\tilde{R}\) is the output of the asymmetric noise suppression and temporal masking modules and \(\tilde{S}\) is the time-averaged, frequency-averaged transfer function.
- spafe.features.pncc.mean_power_normalization(T: ndarray, lam_myu: float = 0.999, nfilts: int = 80, k: int = 1) ndarray[source]#
Apply mean power normalization according to [Kim].
- Parameters
T (numpy.ndarray) – represents the transfer function.
lam_myu (float) – time constant.
nfilts (int) – total number of channels / filters.
k (int) – arbitrary constant.
- Returns
(numpy.ndarray) normalized mean power.
Note
\[ \begin{align}\begin{aligned}\mu[m]=\lambda_{\mu} \mu[m-1]+\frac{(1-\lambda_{\mu})}{L} \sum_{l=0}^{L-1} T[m, l]\\U[m, l]=k \frac{T[m, l]}{\mu[m]}\end{aligned}\end{align} \]where \(\lambda_{\mu}\) is the time constant.
- spafe.features.pncc.asymmetric_noise_suppression_with_temporal_masking(Q_tilde: ndarray, threshold: float = 0) ndarray[source]#
Apply asymmetric noise suppression with temporal masking according to [Kim].
- Parameters
Q_tilde (numpy.ndarray) – array representing the “medium-time power”.
threshold (float) – threshold for the half wave rectifier.
- Returns
(numpy.ndarray) array after asymmetric noise sup and temporal masking.
Note
- 2.1 Apply asymmetric lowpass filtering.
- \[\tilde{Q}_{l e}[m, l]=\mathcal{A} \mathcal{F}_{0.999,0.5}[\tilde{Q}[m, l]]\]
- 2.2 Substract from the input medium-time power.
- \[\tilde{Q}[m, l] - \tilde{Q}_{l e}[m, l]\]
2.3 Pass through an ideal half wave linear rectifier.
2.4 Re-apply asymmetric lowpass filtering.
2.5 Apply temporal masking.
2.6 Switch excitation.
The previous steps can be summarised in the following graph from [Kim].
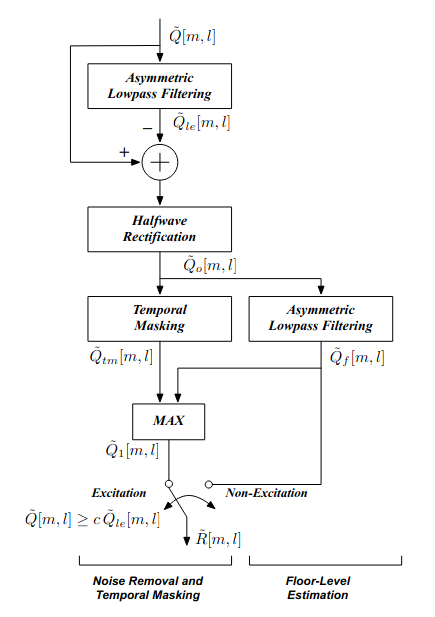
Functional block diagram of the modules for asymmetric noise suppression (ANS) and temporal masking in PNCC processing [Kim].#
- spafe.features.pncc.pncc(sig: ndarray, fs: int = 16000, num_ceps: int = 13, pre_emph: bool = True, pre_emph_coeff: float = 0.97, power=2, window: Optional[SlidingWindow] = None, nfilts: int = 24, nfft: int = 512, low_freq: Optional[float] = 0, high_freq: Optional[float] = None, scale: typing_extensions.Literal[ascendant, descendant, constant] = 'constant', dct_type: int = 2, lifter: Optional[int] = None, normalize: Optional[typing_extensions.Literal[mvn, ms, vn, mn]] = None, fbanks: Optional[ndarray] = None, conversion_approach: typing_extensions.Literal[Glasberg] = 'Glasberg') ndarray[source]#
Compute the Power-Normalized Cepstral Coefficients (PNCCs) from an audio signal, based on [Kim] [Nakamura] .
- Parameters
sig (numpy.ndarray) – a mono audio signal (Nx1) from which to compute features.
fs (int) – the sampling frequency of the signal we are working with. (Default is 16000).
num_ceps (int) – number of cepstra to return. (Default is 13).
pre_emph (bool) – apply pre-emphasis if 1. (Default is True).
pre_emph_coeff (float) – pre-emphasis filter coefficient. (Default is 0.97).
power (int) – power value to use . (Default is 2).
window (SlidingWindow) – sliding window object. (Default is None).
nfilts (int) – the number of filters in the filter bank. (Default is 40).
nfft (int) – number of FFT points. (Default is 512).
low_freq (float) – lowest band edge of mel filters (Hz). (Default is 0).
high_freq (float) – highest band edge of mel filters (Hz). (Default is samplerate/2).
scale (str) – monotonicity behavior of the filter banks. (Default is “constant”).
dct_type (int) – type of DCT used. (Default is 2).
lifter (int) – apply liftering if specified. (Default is None).
normalize (str) – apply normalization if approach specified. (Default is None).
fbanks (numpy.ndarray) – filter bank matrix. (Default is None).
conversion_approach (str) – erb scale conversion approach. (Default is “Glasberg”).
- Returns
2d array of PNCC features (num_frames x num_ceps)
- Return type
Tip
scale: can take the following options [“constant”, “ascendant”, “descendant”].dct: can take the following options [1, 2, 3, 4].normalize: can take the following options [“mvn”, “ms”, “vn”, “mn”].conversion_approach: can take the following options [“Glasberg”]. Note that the use of different options than the default can lead to unexpected behavior/issues.
References
- Kim(1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10)
: Kim C. and Stern R. M., “Power-Normalized Cepstral Coefficients (PNCC) for Robust Speech Recognition,” in IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, vol. 24, no. 7, pp. 1315-1329, July 2016, doi: 10.1109/TASLP.2016.2545928.
- Nakamura
: Nakamura T., An implementation of Power Normalized Cepstral Coefficients: PNCC <https://github.com/supikiti/PNCC>
Note
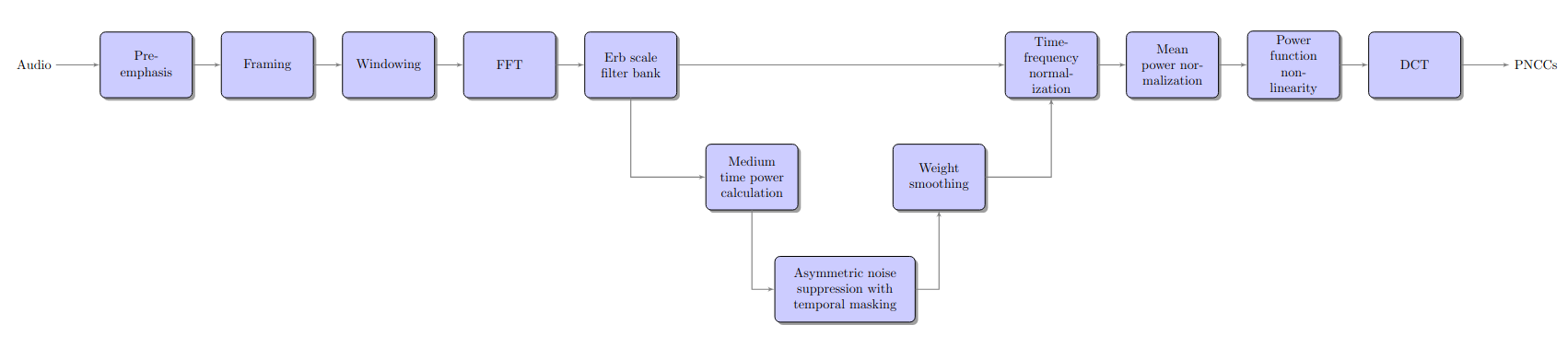
Architecture of power normalized cepstral coefficients extraction algorithm.#
- Examples
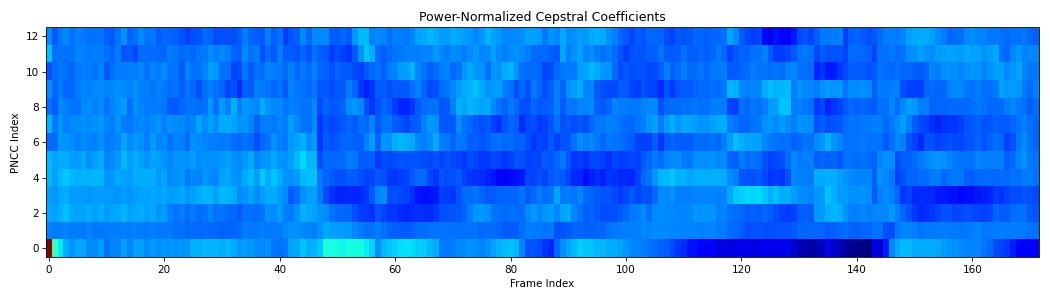
from scipy.io.wavfile import read from spafe.features.pncc import pncc from spafe.utils.preprocessing import SlidingWindow from spafe.utils.vis import show_features # read audio fpath = "../../../tests/data/test.wav" fs, sig = read(fpath) # compute pnccs pnccs = pncc(sig, fs=fs, pre_emph=0, pre_emph_coeff=0.97, window=SlidingWindow(0.03, 0.015, "hamming"), nfilts=128, nfft=1024, low_freq=0, high_freq=fs/2, lifter=0.7, normalize="mvn") # visualize features show_features(pnccs, "Power-Normalized Cepstral Coefficients", "PNCC Index", "Frame Index")