spafe.features.lpc#
Description : Linear Prediction Components and Cepstral Coefficients (LPCs and LPCCs) extraction algorithm implementation.
Copyright (c) 2019-2024 Ayoub Malek. This source code is licensed under the terms of the BSD 3-Clause License. For a copy, see <https://github.com/SuperKogito/spafe/blob/master/LICENSE>.
- spafe.features.lpc.lpc(sig, fs: int = 16000, order=13, pre_emph: bool = True, pre_emph_coeff: float = 0.97, window: Optional[SlidingWindow] = None)[source]#
Compute the Linear prediction coefficents (LPC) from an audio signal.
- Parameters
sig (numpy.ndarray) – a mono audio signal (Nx1) from which to compute features.
fs (int) – the sampling frequency of the signal we are working with. (Default is 16000).
order (int) – order of the LP model and number of cepstral components. (Default is 13).
pre_emph (bool) – apply pre-emphasis if 1. (Default is 1).
pre_emph_coeff (float) – pre-emphasis filter coefficient. (Default is 0.97).
window (SlidingWindow) – sliding window object. (Default is None).
- Returns
(numpy.ndarray) : 2d array of LPC features (num_frames x num_ceps).
(numpy.ndarray) : The error term is the sqare root of the squared prediction error.
- Return type
(tuple)
Note
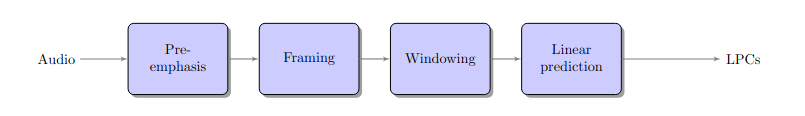
Architecture of linear prediction components extraction algorithm.#
The premis of linear predictive analysis is that the nth sample can be estimated by a linear combination of the previous p samples:
\[xp[n] = -a[1] * x[n-1] - \dots - a[k] * x[n-k] - \dots - a[p] * x[n-p] = - \sum_{k=1}^{p} a_{k} x[n-k]\]where \(xp\) is the predicted signal, \(a_{1}, \dots, a_{p}\) are the predictor coefficients, \(p\) is the model order, and \(n\) is the sample index. Based on the previous equation, we can estimate the prediction error as follows [Ucl-brain]:
\[e[n] = x[n] - xp[n] \implies x[n] = e[n] + \sum_{k=1}^{p} a_{k} x[n-k]\]The unknown here are the LP coefficients \(a\), hence we need to minimize e to find those. We can further rewrite the previous equations for all samples [Collomb]:
\[E = \sum_{i=1}^{N} \left( x[i] - \sum_{k=1}^{p} a_{k} x[i-k] \right)^2\]All the previous steps can be presented in a matrix, which is a Toeplitz matrix \(R.A = 0\)
References
- Darconis
: Draconi, Replacing Levinson implementation in scikits.talkbox, Stackoverflow, https://stackoverflow.com/a/43457190/6939324
- Cournapeau
: David Cournapeau D. talkbox, https://github.com/cournape/talkbox
- Menares
: Menares E. F. M., ML-experiments, https://github.com/erickfmm/ML-experiments
- Collomb
: Collomb C. Linear Prediction and Levinson-Durbin Algorithm, 03.02.2009, <https://www.academia.edu/8479430/Linear_Prediction_and_Levinson-Durbin_Algorithm_Contents>
- Ucl-brain
: Ucl psychology and language sciences, Faculty of brain Sciences, Unit 8 linear prediction <https://www.phon.ucl.ac.uk/courses/spsci/dsp/lpc.html>
- Examples
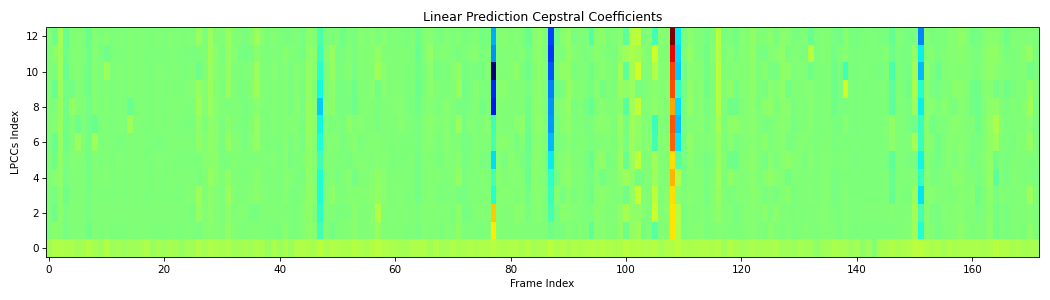
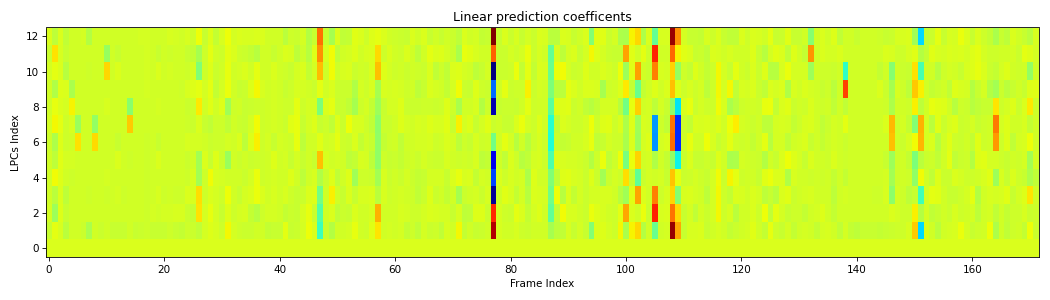
from scipy.io.wavfile import read from spafe.features.lpc import lpc from spafe.utils.preprocessing import SlidingWindow from spafe.utils.vis import show_features # read audio fpath = "../../../tests/data/test.wav" fs, sig = read(fpath) # compute lpcs lpcs, _ = lpc(sig, fs=fs, pre_emph=0, pre_emph_coeff=0.97, window=SlidingWindow(0.030, 0.015, "hamming")) # visualize features show_features(lpcs, "Linear prediction coefficents", "LPCs Index", "Frame Index")
- spafe.features.lpc.lpc2lpcc(a, e, nceps)[source]#
Convert linear prediction coefficents (LPC) to linear prediction cepstral coefficients (LPCC) as described in [Rao] and [Makhoul].
- Parameters
a (numpy.ndarray) – linear prediction coefficents.
order (int) – linear prediction model order.
nceps (int) – number of cepstral coefficients.
- Returns
linear prediction cepstrum coefficents (LPCC).
- Return type
Note
\[\begin{split}C_{m}=\left\{\begin{array}{l} log_{e}(p), & \text{if } m = 0 \\ a_{m} + \sum_{k=1}^{m-1} \frac{k}{m} C_{m} a_{m-k} , & \text{if } 1 <= m <= p \\ \sum_{k=m-p}^{m-1} \frac{k}{m} C_{m} a_{m-k} , & \text{if } m > p \end{array}\right.\end{split}\]References
- Makhoul
: Makhoul, J. (1975). Linear prediction: A tutorial review. Proceedings of the IEEE, 63(4), 561–580. doi:10.1109/proc.1975.9792
- Rao
: Rao, K. S., Reddy, V. R., & Maity, S. (2015). Language Identification Using Spectral and Prosodic Features. SpringerBriefs in Electrical and Computer Engineering. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-17163-0
- spafe.features.lpc.lpcc(sig: ndarray, fs: int = 16000, order=13, pre_emph: bool = True, pre_emph_coeff: float = 0.97, window: Optional[SlidingWindow] = None, lifter: Optional[int] = None, normalize: Optional[typing_extensions.Literal[mvn, ms, vn, mn]] = None) ndarray[source]#
Computes the linear predictive cepstral components / coefficents from an audio signal.
- Parameters
sig (numpy.ndarray) – input mono audio signal (Nx1).
fs (int) – the sampling frequency of the signal. (Default is 16000).
order (int) – order of the LP model and number of cepstral components. (Default is 13).
pre_emph (bool) – apply pre-emphasis if 1. (Default is 1).
pre_emph_coeff (float) – pre-emphasis filter coefficient. (Default is 0.97).
window (SlidingWindow) – sliding window object. (Default is None).
lifter (int) – apply liftering if specified. (Default is None).
normalize (str) – apply normalization if provided. (Default is None).
- Returns
2d array of LPCC features (num_frames x num_ceps)
- Return type
Tip
normalize: can take the following options [“mvn”, “ms”, “vn”, “mn”].
Note
Returned values are in the frequency domain
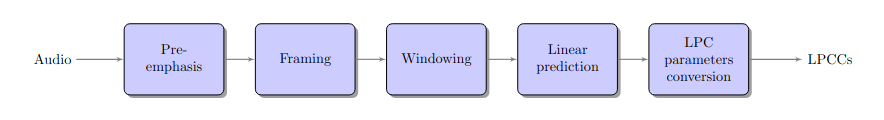
Architecture of linear prediction cepstral coefficients extraction algorithm.#
- Examples
from scipy.io.wavfile import read from spafe.features.lpc import lpcc from spafe.utils.preprocessing import SlidingWindow from spafe.utils.vis import show_features # read audio fpath = "../../../tests/data/test.wav" fs, sig = read(fpath) # compute lpccs lpccs = lpcc(sig, fs=fs, pre_emph=0, pre_emph_coeff=0.97, window=SlidingWindow(0.03, 0.015, "hamming")) # visualize features show_features(lpccs, "Linear Prediction Cepstral Coefficients", "LPCCs Index","Frame Index")